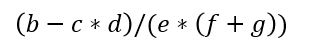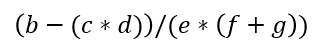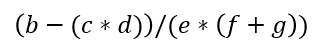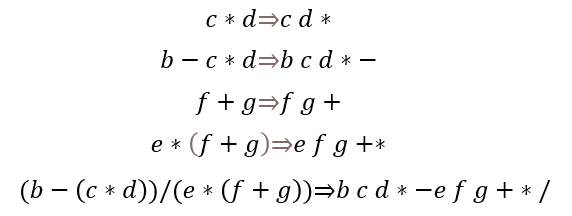记录学习过程中遇到的各种知识点
移位运算 一、右移 C语言标准并没有明确定义对于有符号数应该使用哪种类型的右移——算术右移或者逻辑右移都可以。不幸地,这就意味着任何假设一种或者另一种右移形式的代码都可能会遇到可移植性问题。然而,实际上,几乎所有的编译器/机器组合都对有符号数使用算术右移 ,且许多程序员也假设机器会使用这种右移。另一方面,对于无符号数,右移必须是逻辑的。
与C相比,Java对于如何进行右移有明确的定义。表达式$x>>k$会将$x$算术右移$k$个位置,而$x>>>k$会对$x$做逻辑右移
二、移动k位(k很大) 对于一个由$w$位组成的数据类型,如果要移动$k \ge w$位会得到什么结果呢?例如,思考下面的表达式会得到什么结果:
1 2 3 int lval = 0x12345678 << 32 ;int aval = 0xFEDCBA98 >> 36 ;unsigned uval = 0xFEDCBA98 u >> 40 ;
在许多机器上,当移动一个$w$位的值时,移位指令只考虑位移量的低$\log_2w$位,因此实际上位移量就是通过计算$k$ mod $w$得到的,例如,当$w=32$时,上面三个位移运算分别是移动0、4、8位,得到结果:
1 2 3 lval 0 x12345678 ;aval 0 xFFEDCBA9 ;uval 0 x00 FEDCBA;
我的理解 假设数据类型是32位的,绝大多数情况下左移(或右移)的$k$值都在0至31之间,所以系统只“安排”了5个bit来负责记录移位时的$k$值,因此当试图移位32位(甚至更多位)时,由于只有5个bit负责此事,相当于令$k$对32取模,取模结果为实际移动位数。同理数据类型为64位时,系统(应该会)“安排”6个bit负责记录移位的$k$值,相当于令$k$对64取模。
前中后缀表达式 平时计算所使用的表达式都是中缀表达式,如
而这样的带有括号以及区分优先级的表达式对计算机而言却难以计算
于是考虑将其转为前缀表达式(波兰式)或后缀表达式(逆波兰式)
转换 以中缀表达式
为例,考虑将其转换为前缀表达式
方法一:直接转换 1.首先按运算顺序层层给表达式加上括号
2.从最里层括号开始,忽略括号,符号在前,数字在后
再考虑将其转换为后缀表达式
1.首先按运算顺序层层给表达式加上括号
2.从最里层括号开始,忽略括号,数字在前,符号在后
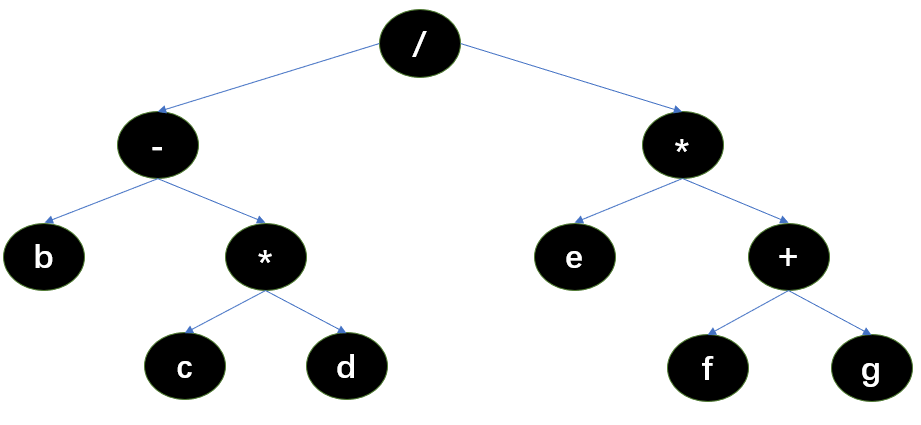
方法二:利用表达式树 将中缀表达式转换为表达式树,叶子节点是数值,非叶子节点为符号。则先序遍历、中序遍历与后序遍历分别对应前缀表达式、中缀表达式与后缀表达式
建树时,一般选择根节点为优先级最低且居于表达式正中的符号
代码实现 对于任意两种类型的表达式间相互转换,均可使用栈实现
只需分别定义一个操作数栈和操作符栈,规定好各符号在栈内外优先级即可
Warshall算法 1962年,S.Warshall提出了一个计算传递闭包关系矩阵的有效方法,可以在计算机上编程实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 void Warshall (int m[][]) for (int j = 0 ;j < n;j++) for (int i = 0 ;i < n;i++) if (m[i][j]) for (int k = 0 ;k < n;k++) m[i][k] = m[i][k] | m[j][k]; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 #include <iostream> using namespace std ;int n;int ** _Matrix;void Init () cout << "Enter matrix size:" ; cin >> n; _Matrix = new int * [n]; for (int i = 0 ;i < n;i++) _Matrix[i] = new int [n]; cout << "Enter the elements line by line:" ; for (int i = 0 ;i < n;i++) for (int j = 0 ;j < n;j++) cin >> _Matrix[i][j]; } void Warshall (int ** m) cout << endl ; for (int j = 0 ;j < n;j++) for (int i = 0 ;i < n;i++) if (m[i][j]) for (int k = 0 ;k < n;k++) m[i][k] = m[i][k] | m[j][k]; } void Print () for (int i = 0 ;i < n;i++) { for (int j = 0 ;j < n;j++) cout << _Matrix[i][j] << " " ; cout << endl ; } } int main () Init(); Warshall(_Matrix); Print(); return 0 ; }
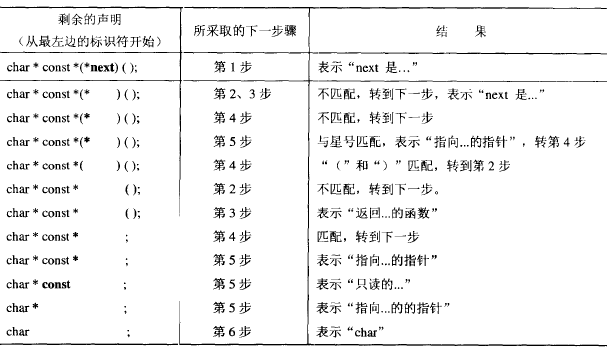
声明解释器 说明 用来解释声明的一个小玩意
作用:输入一个声明,程序解释该声明
代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <ctype.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define MAXTOKENS 100 #define MAXTOKENLEN 64 enum type_tag {struct token { char type; char string [MAXTOKENLEN]; }; int top = -1 ; struct token stack [MAXTOKENS ];struct token this ;struct token pop ( void ) { return stack [top--]; } void push ( struct token t ) stack [++top] = t; } enum type_tag classify_string ( void ) char *s = this .string ; if ( !strcmp ( s, "const" ) ) { strcpy ( s, "read-only" ); return QUALIFIER; } if ( !strcmp ( s, "volatile" ) ) return QUALIFIER; if ( !strcmp ( s, "void" ) ) return TYPE; if ( !strcmp ( s, "signed" ) ) return TYPE; if ( !strcmp ( s, "unsigned" ) ) return TYPE; if ( !strcmp ( s, "char" ) ) return TYPE; if ( !strcmp ( s, "short" ) ) return TYPE; if ( !strcmp ( s, "int" ) ) return TYPE; if ( !strcmp ( s, "long" ) ) return TYPE; if ( !strcmp ( s, "float" ) ) return TYPE; if ( !strcmp ( s, "double" ) ) return TYPE; if ( !strcmp ( s, "struct" ) ) return TYPE; if ( !strcmp ( s, "union" ) ) return TYPE; if ( !strcmp ( s, "enum" ) ) return TYPE; return IDENTIFIER; } void gettoken () char *p = this .string ; while ( ( *p = getchar() ) == ' ' ) ; if ( isalnum ( *p ) ) { while ( isalnum ( *++p = getchar() ) ) ; ungetc( *p, stdin ); *p = '\0' ; this .type = classify_string(); return ; } if ( *p == '*' ) { strcpy ( this .string , "pointer to" ); this .type = '*' ; return ; } this .string [1 ] = '\0' ; this .type = *p; } void read_to_first_identifier () gettoken(); while ( this .type != IDENTIFIER ) { push( this ); gettoken(); } printf ( "%s is " , this .string ); gettoken(); } void deal_with_function_args () while ( this .type != ')' ) gettoken(); gettoken(); printf ( "function returning " ); } void deal_with_arrays () while ( this .type == '[' ) { printf ( "array " ); gettoken(); if ( isdigit ( this .string [0 ] ) ) { printf ( "0.. %d " , atoi(this .string ) - 1 ); gettoken(); } gettoken(); printf ( "of " ); } } void deal_with_any_pointers () while ( stack [top].type == '*' ) { printf ( "%s " , pop().string ); } } void deal_with_declarator () switch ( this .type ) { case '[' : deal_with_arrays(); break ; case '(' : deal_with_function_args(); break ; } deal_with_any_pointers(); while ( top >= 0 ) { if ( stack [top].type == '(' ) { pop(); gettoken(); deal_with_declarator(); } else printf ( "%s " , pop().string ); } } int main () read_to_first_identifier(); deal_with_declarator(); printf ( "\n" ); return 0 ; }
效果 1 2 3 fez@papyruszzz:~$ ./cdecl int * const (*next[])() next is array of pointer to function returning read-only pointer to int